
This study showed statistically significant differences in the ankle mortise coronal and sagittal angles among the 3 groups. After the deviation of the load force line of ankle joint, the stress distribution of the ankle joint may be changed, resulting in a disorder of the bone joint load and causing arthritis in ankle joint. When the distal tibia is damaged by high-energy injury, the accompanying fibula often has a fracture shift, and the perpendicular line of the connection line of the two fornix tops of ankle mortise no longer maintains an approximately right angle with the connection line between the anterior and posterior ankle margins, thus exhibiting the changes of coronal and sagittal angles of ankle mortise. 18 In this study, the coronal angle of the ankle mortise on the uninjured side was 6.04° ± 1.17°, and the sagittal angle was 11.28° ± 2.81°, which is the load force line of the normal ankle joint. 17 Anatomically, the ankle mortise angle change reflects the change in the load force line of the ankle joint. The causes for the angle change of ankle mortise include poor restoration of anterior lateral bone mass (Cha-put nodule) at the lower end of tibia uneven tibia bone graft filling improper selection of a steel plate and uneven support and premature load of the ankle joint. The 1/2 osteotomy at the lower end of tibia is equivalent to 65% of the normal contact area of ankle joint. 16 For the patients with mediocre + poor scores of ankle joint function, the depth difference of ankle mortise between affected and uninjured sides was 2–5 mm. 15 The reasons for the depth change of ankle mortise include rupture fracture at the lower end of tibia causing the fracture block to be separated at the sagittal plane and not dissected and fixed during treatment and displacement of the posterior bone block of distal tibia being difficult to expose during surgery, causing dissatisfactory fixation. 14 Zhang et al found that when the distal tibia fracture block was greater than or equal to 10% of the articular surface of the tibial fracture, surgical reduction and fixation of the posterior fracture block were required. 13 Hak et al confirmed by biomechanical experiments that the posterior malleolar fracture can cause the stress center of the ankle joint contact to move forward and inward, so that it withstands huge contact stress during exercises, causing traumatic arthritis of the ankle joint. The depth of ankle mortise increases, causing the astragalus to sink deep inside, and the front is prone to collide and affect joint activity. 11, 12 Herein, the 2-year follow-up results showed that 7 patients in the mediocre + poor group had Mazur scores of the ankle joint of 2 mm on the uninjured side, which indicates that the width changes of ankle mortise has a greater impact on the function of the ankle joint in the future. 10 The reasons for the change in width of ankle mortise include reduction of malleolus medialis fracture, less than ideal displacement of the fibula or lateral malleolus fracture no reduction or fixation performed on the tibiofibular syndesmosis separation and a compressed burst fracture at the lower end of tibia end that was not retracted during transverse separation and reduction.

9 Moreover, after the widening of ankle mortise, its restrictive effect on the astragalus is weakened, which results in anterior and posterior instability, eventually leading to ankle joint traumatic arthritis.

The pairwise q test revealed that there were statistically significant differences among the 3 groups in intraoperative ankle mortise depth and coronal and sagittal angles ( P < 0.05 Table 3), suggesting all these factors had significant impact on postoperative outcomes.Īn increase in the width of ankle mortise causes the astragalus to move outward in ankle mortise, resulting in instability of the lateral side of ankle joint, loss of anastomosis on the articular surface, reduction of the weight-bearing area, and uneven pressure, which aggravates ischemia and cartilage degeneration. In addition, the differences in the ankle mortise depth and coronal and sagittal angles were statistically significant among the 3 groups ( P < 0.05 Table 2).
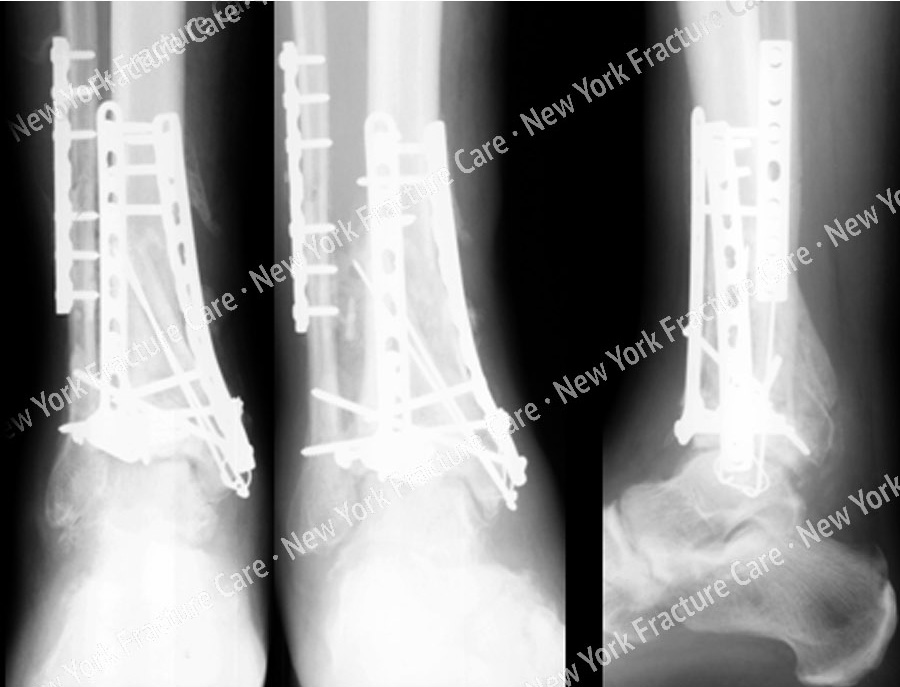
Therefore, the width of ankle mortise during surgery had a significant effects on postoperative outcomes. The difference in the width of ankle mortise was statistically significant among the 3 groups ( P 2 mm on average and that of the excellent and good groups was <1 mm. There was no significant difference in the height difference among the 3 groups ( P > 0.05 Table 2), suggesting that the recovery of ankle joint function was not highly correlated with the height of ankle mortise.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
